
7 November 2023
South Africa’s Constitutional Court is failing to deliver judgments on time. Archive photo: Ashraf Hendricks
The Constitutional Court is setting a poor example by failing to deliver judgments timeously. South Africa’s apex court currently has four late judgments outstanding and many others have been delivered late this year. Moreover, the court’s website is poorly maintained, making it hard to know the status of cases.
The judicial norms and standards explain that judgments in both civil and criminal matters should generally not be reserved without a fixed date for handing them down.
But instead of delivering judgment immediately or soon after a hearing or the end of a trial, the court may decide to reserve judgment without a fixed date for handing it down.
The judicial norms and standards state that except for “exceptional cases where it is not possible to do so, every effort shall be made to hand down judgments no later than three months after the last hearing”.
GroundUp started reporting on late judgments in 2017 and we have used a more lenient six-month benchmark to classify a reserved judgment as late.
According to the last available Reserved Judgment Report for the Chief Justice, as of 31 December 2022, 181 judgments were outstanding for at least six months in courts across the country. In total, 901 judgments were reserved.
GroundUp has also started tracking the list of late judgments. Of judgments reserved by the Constitutional Court since August last year and that have since been handed down (delivered), ten were late using the six-month criterion. 19 were delivered late using the judicial norms and standard’s three-month criterion.
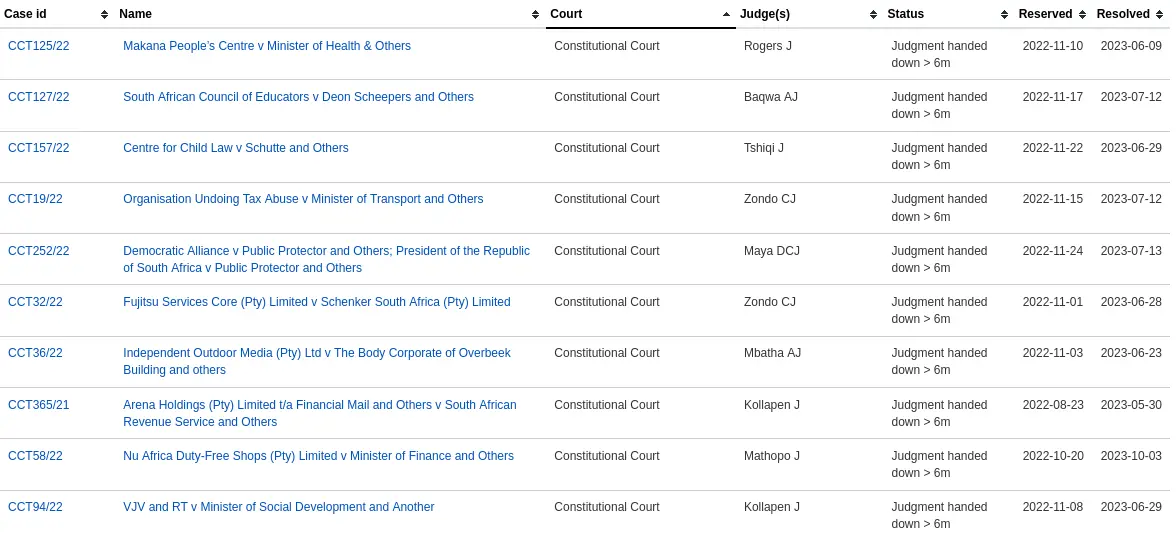
These are the ten Constitutional Court judgments listed on our system that were reserved since August 2022 and subsequently handed down more than six months after they were reserved, in breach of the Office of the Chief Justice’s norms and standards.
After GroundUp asked the Office of the Chief Justice (OCJ) last week about the 21 matters listed as “still awaiting judgment” on the Constitutional Court’s website, it seems to have been updated. The site now lists 18 outstanding judgments.
But some of the cases listed are years old even though they have been finalised, and other matters where we know judgments have already been delivered still feature on this list.
For example, judgment in Sasol Chevron Holdings and the Commissioner for the South African Revenue Service (SARS) was reserved on 4 May 2023. Judgment was handed down on 3 October 2023, but the Constitutional Court website still has it listed as awaiting judgment.
Another example is the matter between the South African Social Security Agency (SASSA) and life insurance company Lion of Africa over deductions from children’s grants. Judgment was already delivered on 26 May 2016, yet, it is listed as awaiting judgment on the court’s website. The site also lists Bonginkosi Khanyile v The State as reserved on 1 March 2017, but we understand that an order for this case was handed down.
Based on the Constitutional Court’s outstanding judgments list and excluding the above, there are four judgments reserved more than than six months ago that are still outstanding:
GroundUp contacted the OCJ to establish which cases at the Constitutional Court had already been handed down and which were still outstanding. We sent questions more than a week ago and regularly followed up with the OCJ. The OCJ’s media team apologised for the delay and advised us that our enquiry “is receiving attention”. After sending several more requests for comment this week, the OCJ has stopped responding.